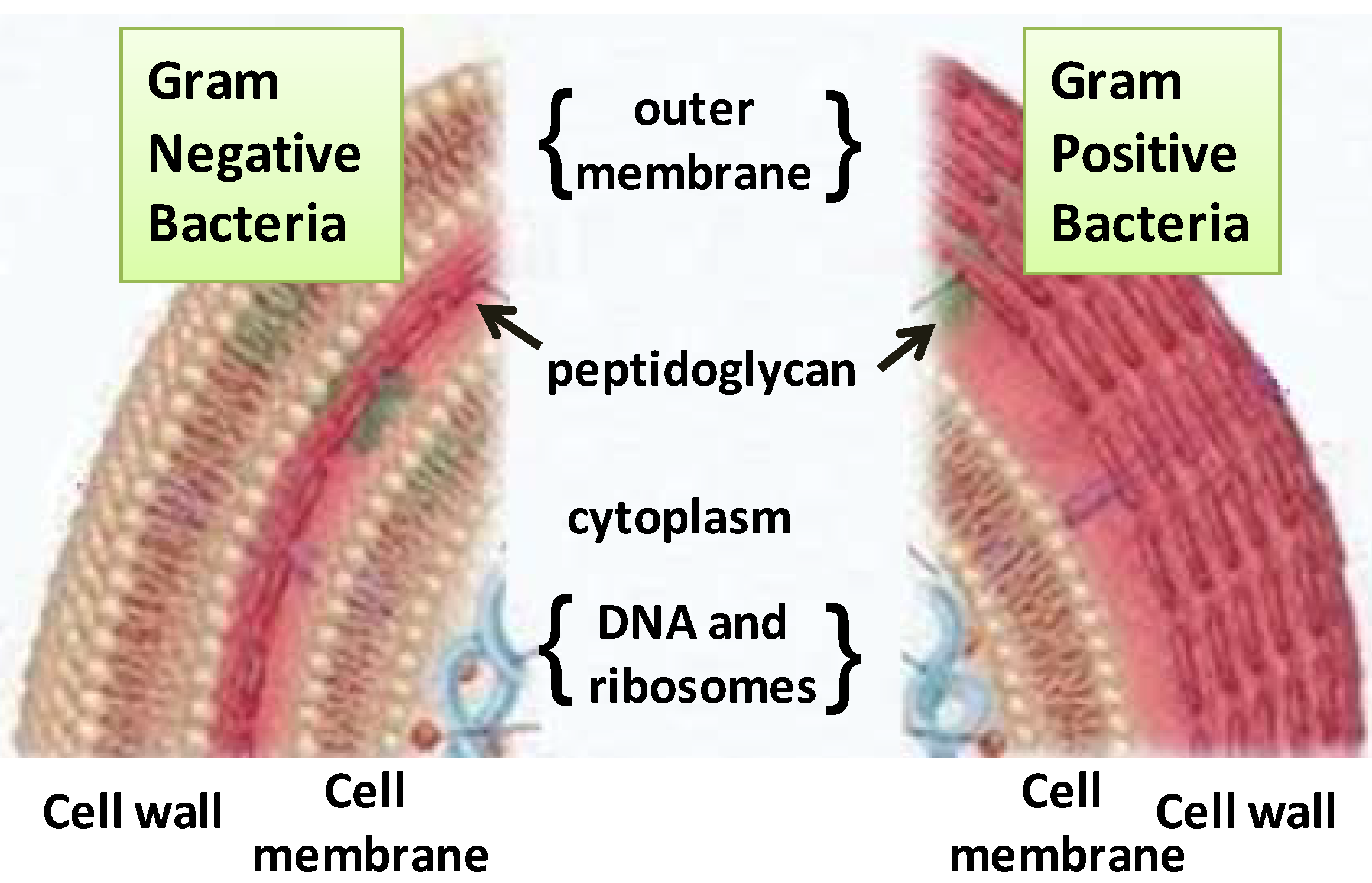
Cell Membrane Structure Journal
A cell membrane is not a lamellar phase but a real object whose structure corresponds more or less to a lamellar phase.
Cell membrane structure journal. Recent studies indicate that the cell membrane interacting with its attached cytoskeleton is an important regulator of cell function exerting and responding to forces. Ad Reveal the Subcellular Localization in Cell Imaging Applications. Red Cell Antigens and Antibodies ed.
THE CELL MEMBRANE 1. Alexa Fluor Dye Conjugates. Introduction The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the intracellular environment from.
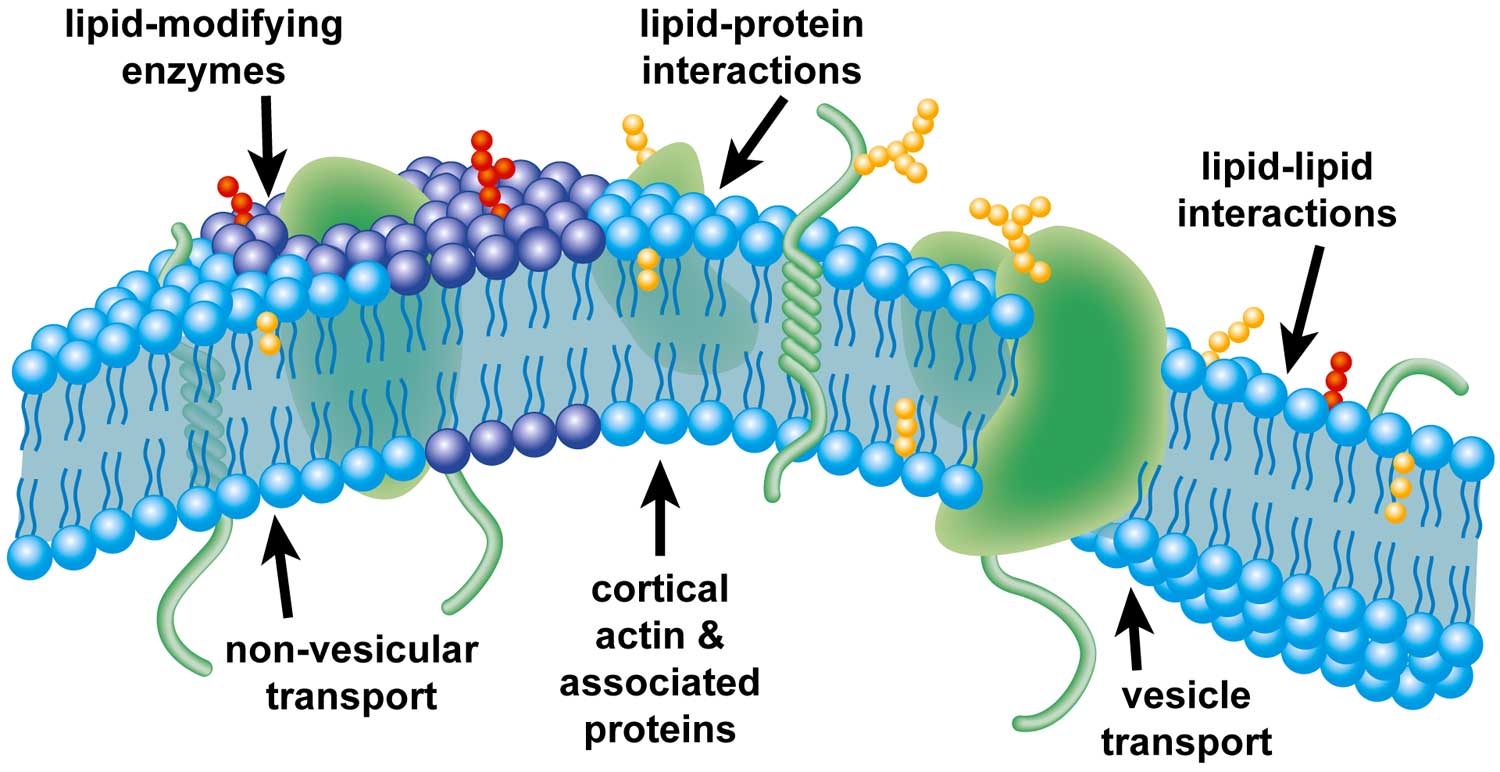
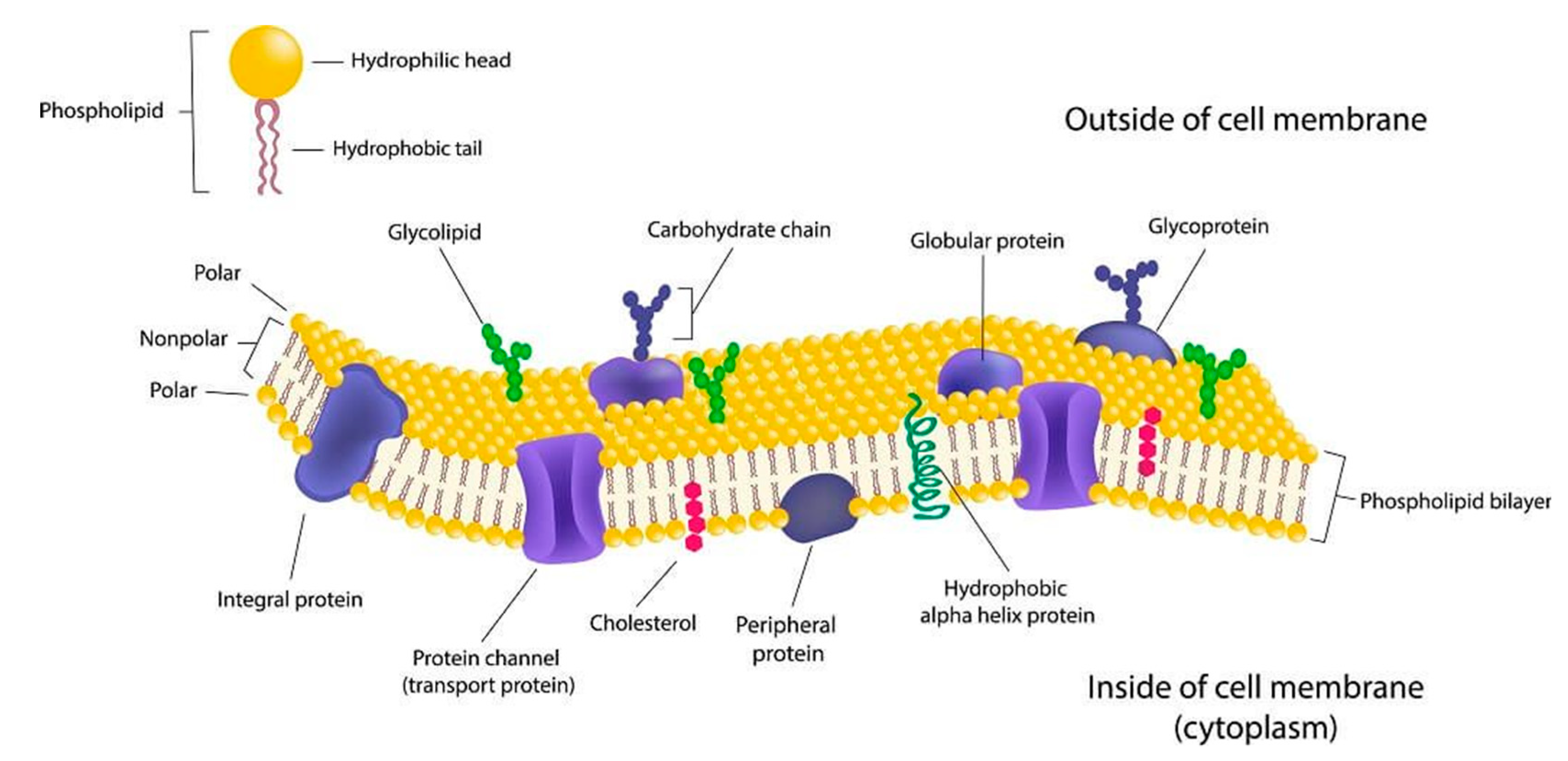
This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Considerable progress has been made in understanding the roles played by two membrane lipids. The fascination of membrane research is that the functionality of the cell membrane is dependent on the carefully orchestrated and mutually interdependent properties of lipids and proteins.
Recent studies of structure-function relationships in biological membranes have revealed fundamental concepts concerning the regulation of cellular membrane function by membrane lipids. This Selectively Permeable membrane regulates what passes into and out of the cell. Our editorial process.
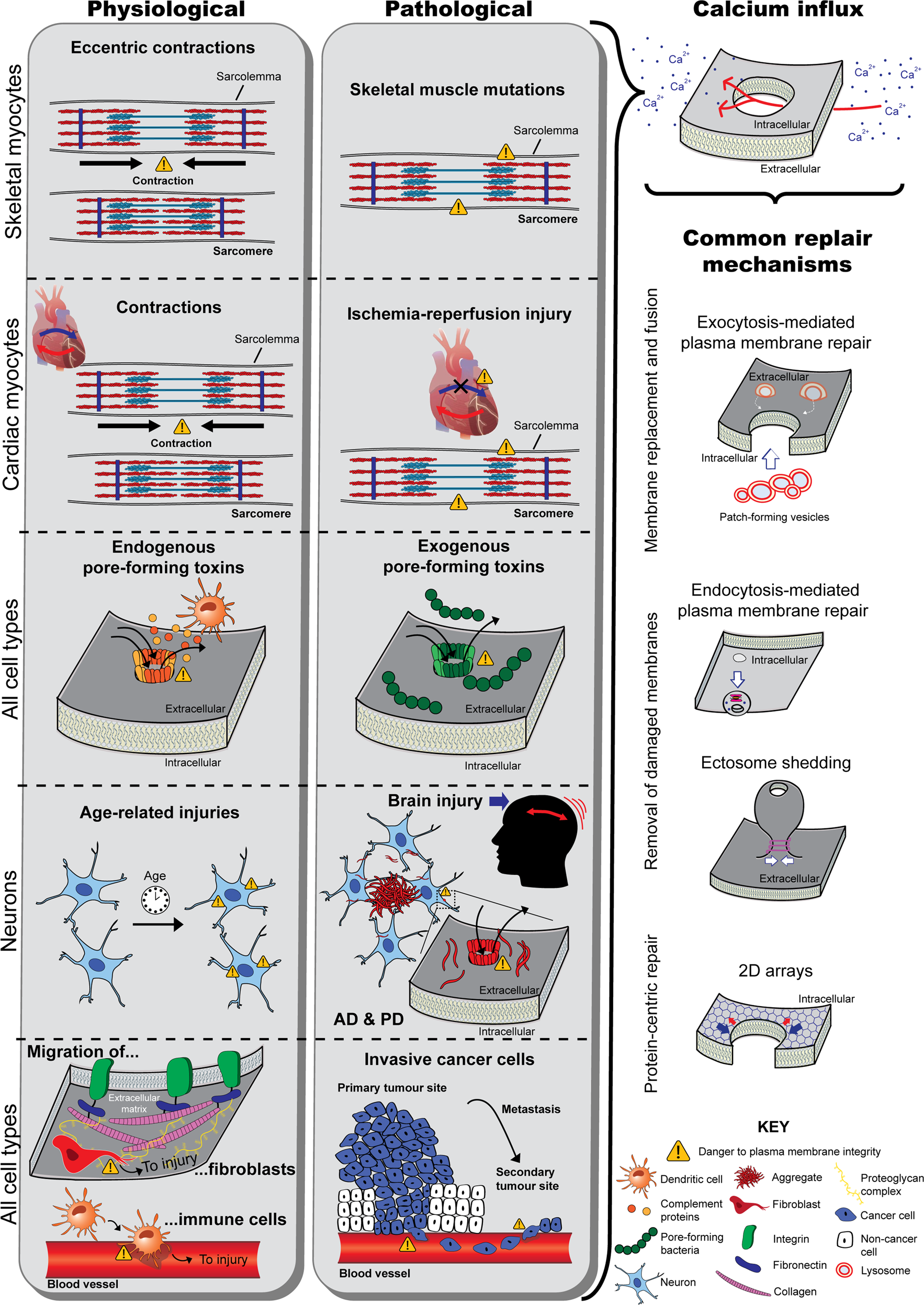
2 proteins aggregate to form islands evenly dispersed at the cytoplasmic side of the cell membrane with a height of 1012 nm. Original Research Cell membranes are commonly considered fundamental structures having multiple roles such as confinement storage of lipids sustain and control of membrane proteins. J D Robertson.
Thefluid mosaic model ofthe cell membrane. The current views on the structure and function of biological membranes the role of their lipid protein and carbohydrate components in the maintenance of cell vital activity are summarized. Garratty G pp.