Cellular Respiration Formula Explained

Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy.
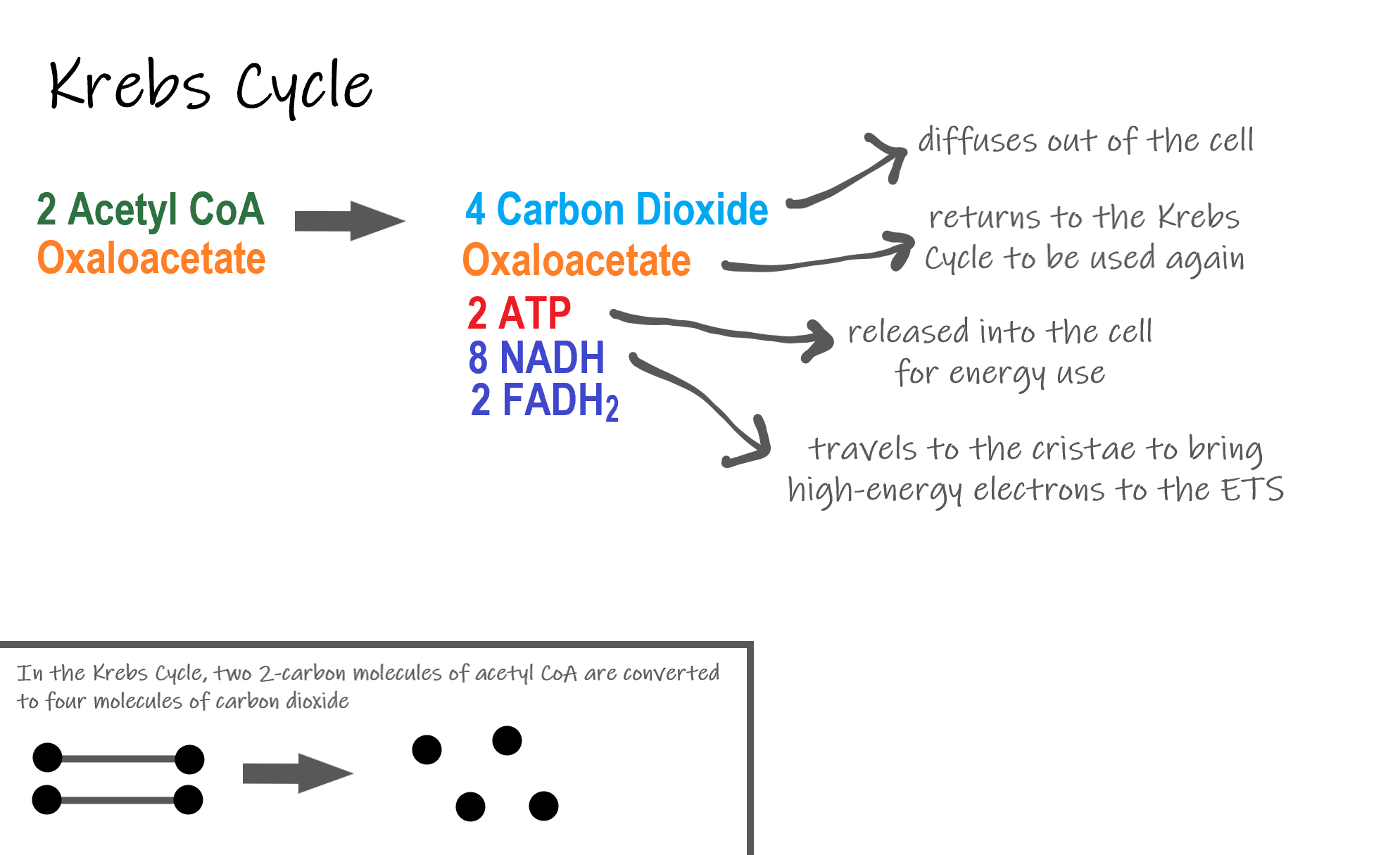
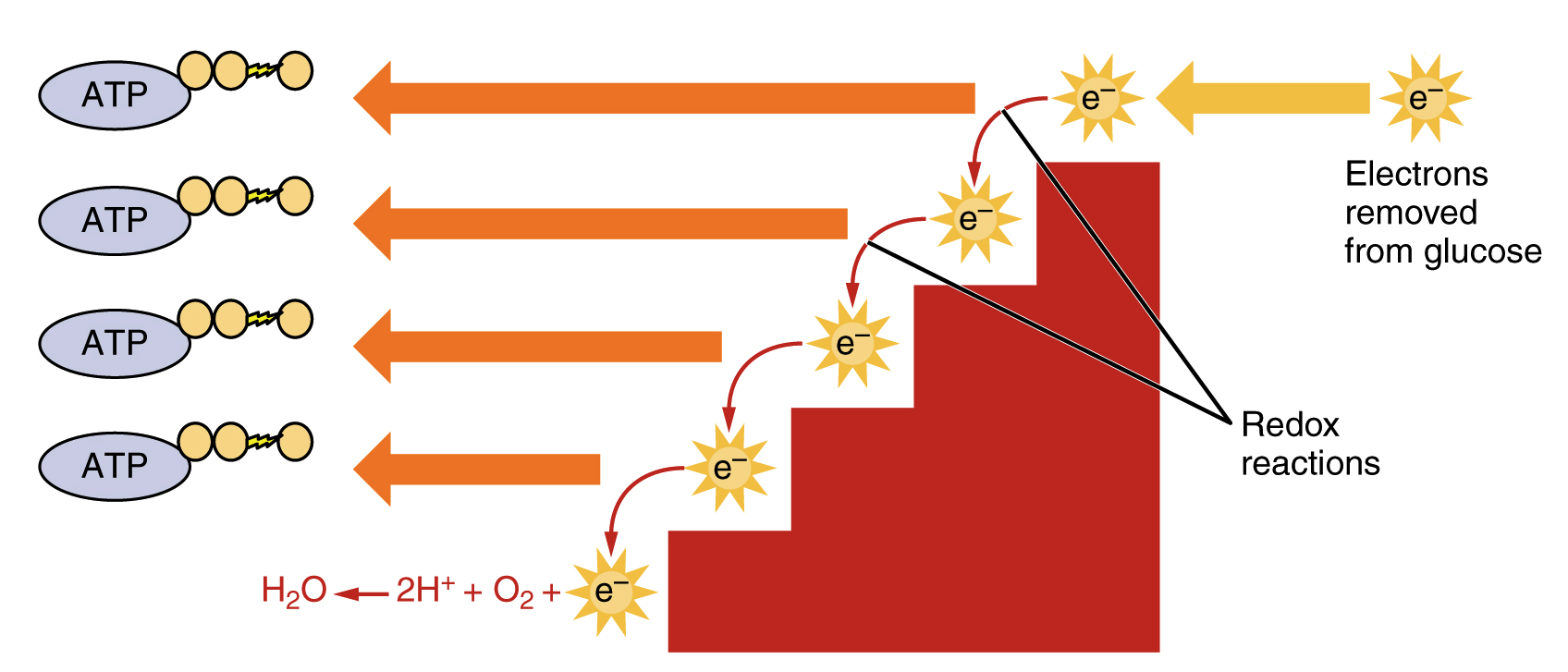
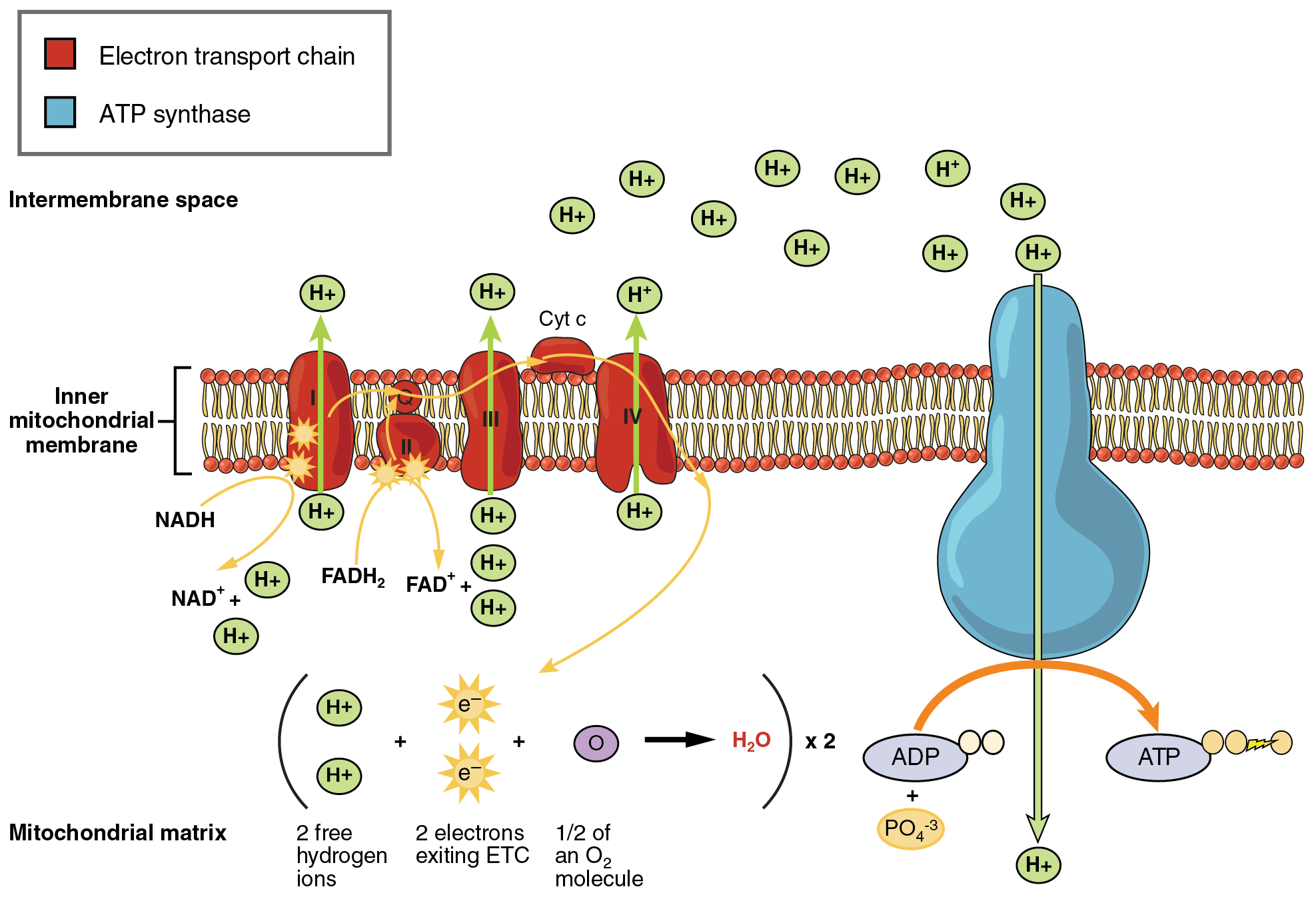
Cellular respiration formula explained. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In summary cellular respiration is a process that cells use to make energy. C 6 H 12 O 6 glucose 6O 2 36 ADP depleted ATP 36 P i phosphate groups 6CO 2 6H 2 O 36 ATP.
Chemical structures of nad and nadh. Cellular respiration formula explained. It is important to know that the equation listed above is a summary equation.
Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Respiration is of two types aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and ADP to produce carbon dioxide water and ATP.
During this activity the students work with a group to discuss the compounds and conditions that need to be present in order. This is the balanced equation that yields energy. Adenosine triphosphate chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
Cellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. There are three main stages of cellular respiration.
Such processes are explained below. ENE1L5 EK ENE1L7 EK Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions which break large molecules into smaller ones releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds in.