Cellular Respiration Takes Place In Two Stages
/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)
Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes.
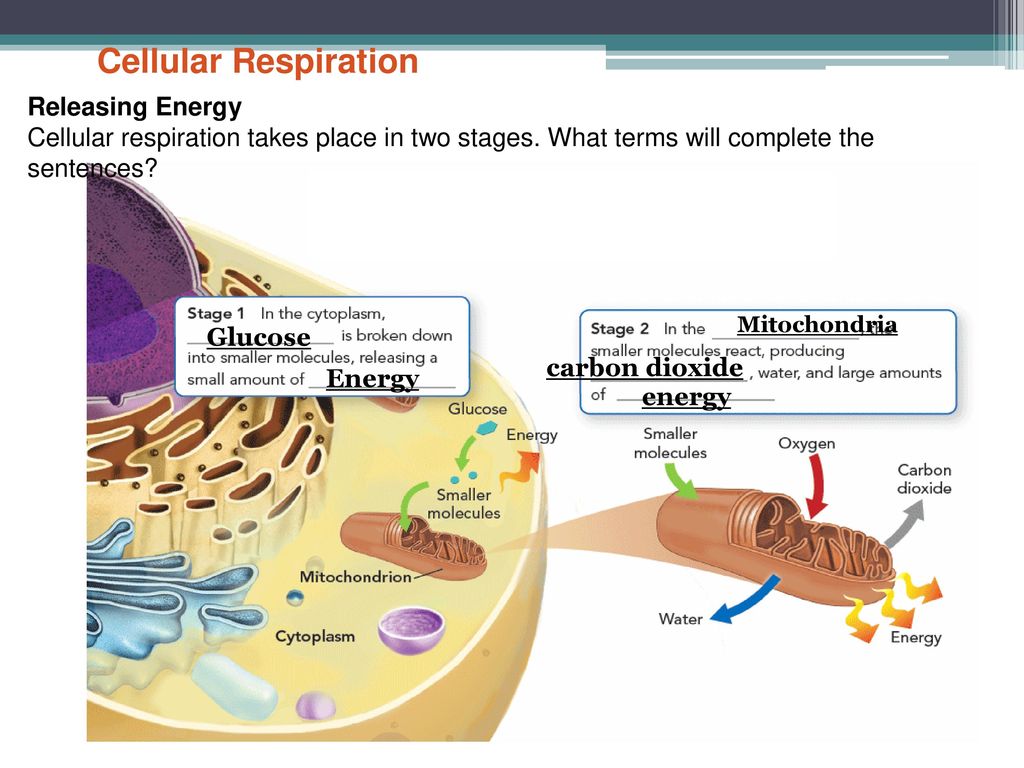
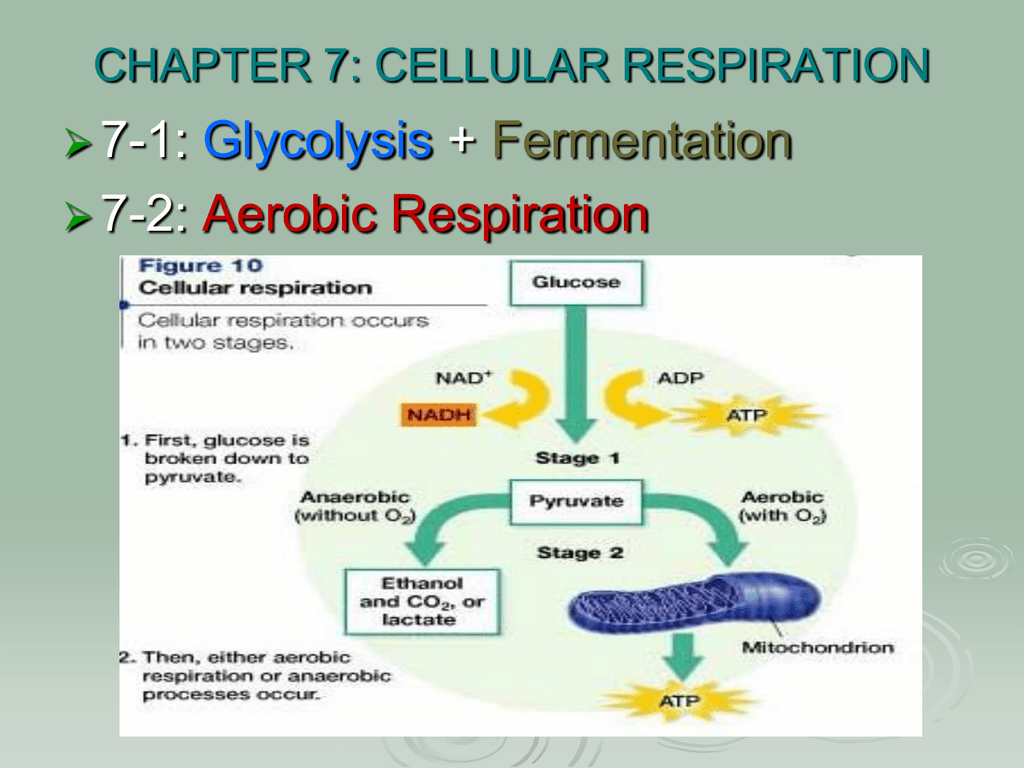
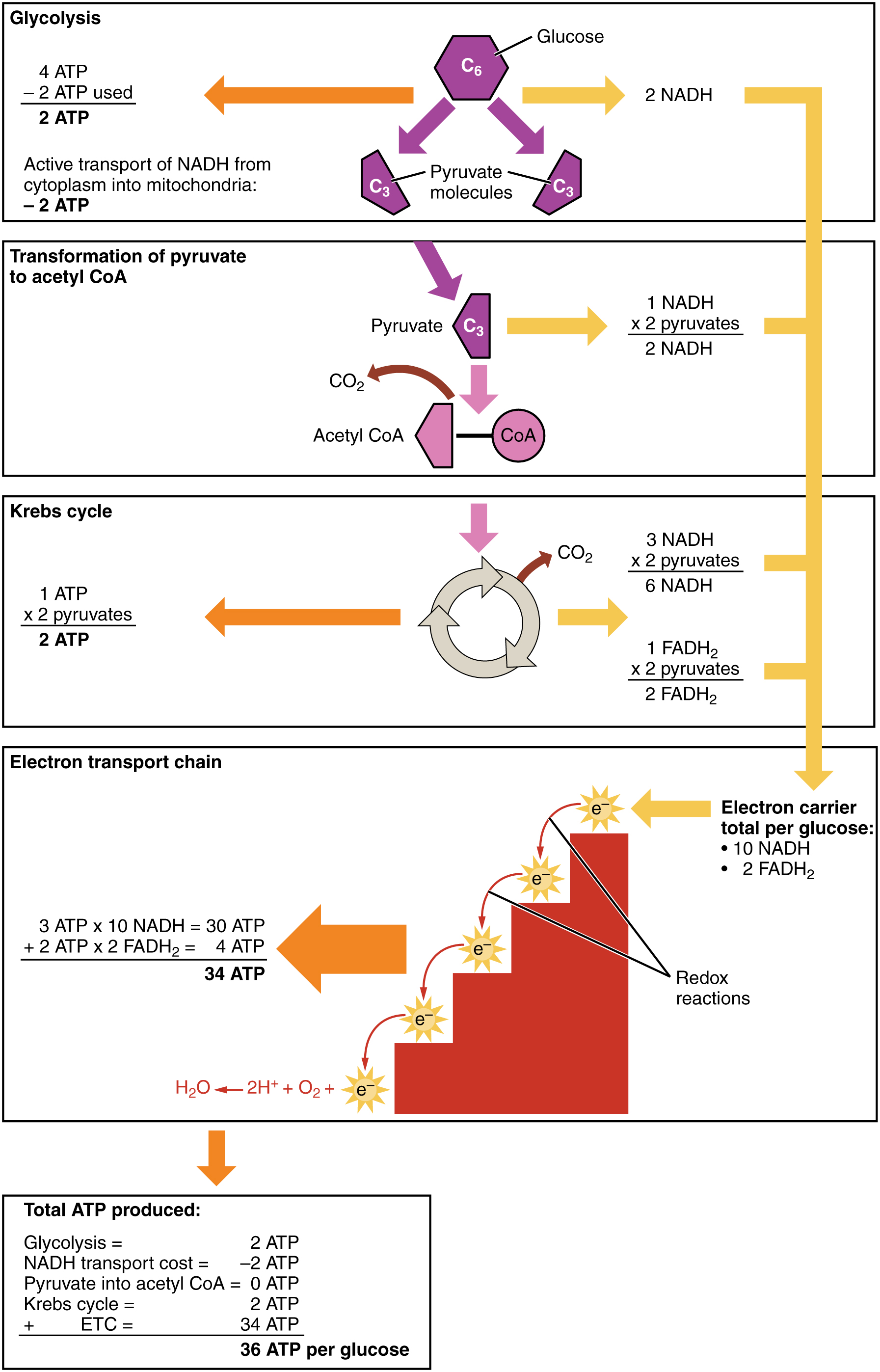
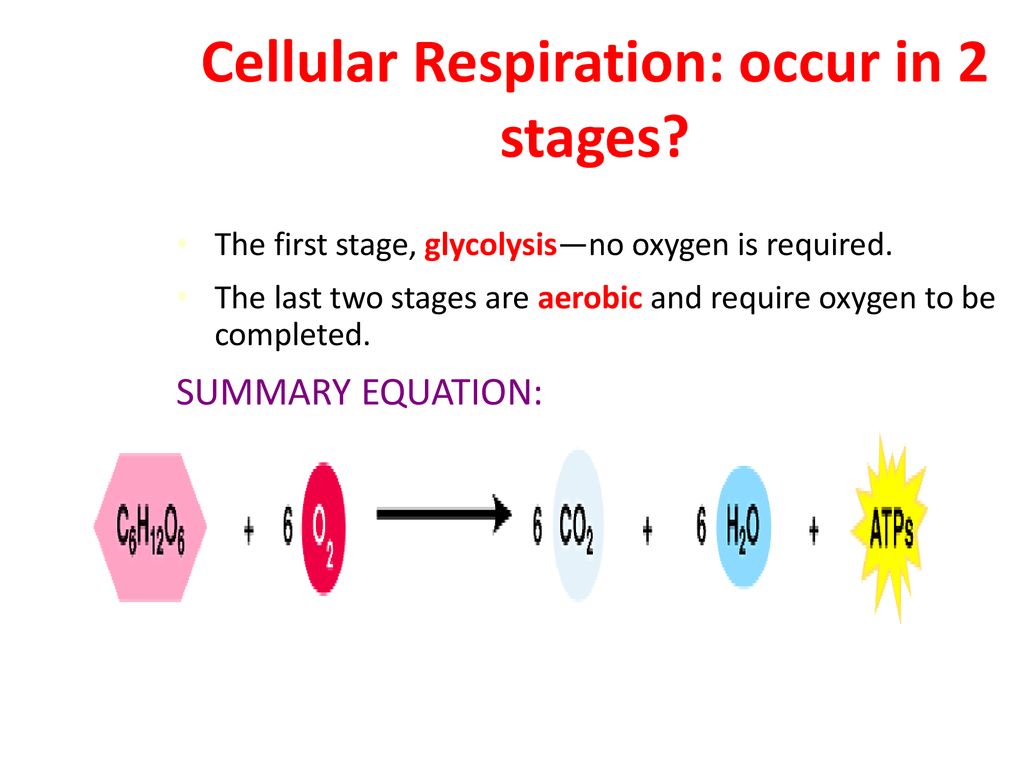
Cellular respiration takes place in two stages. Glycolysis is an anaerobic. Are transferred to molecules of NAD to produce two molecules of NADH. There are three main stages of cellular respiration.
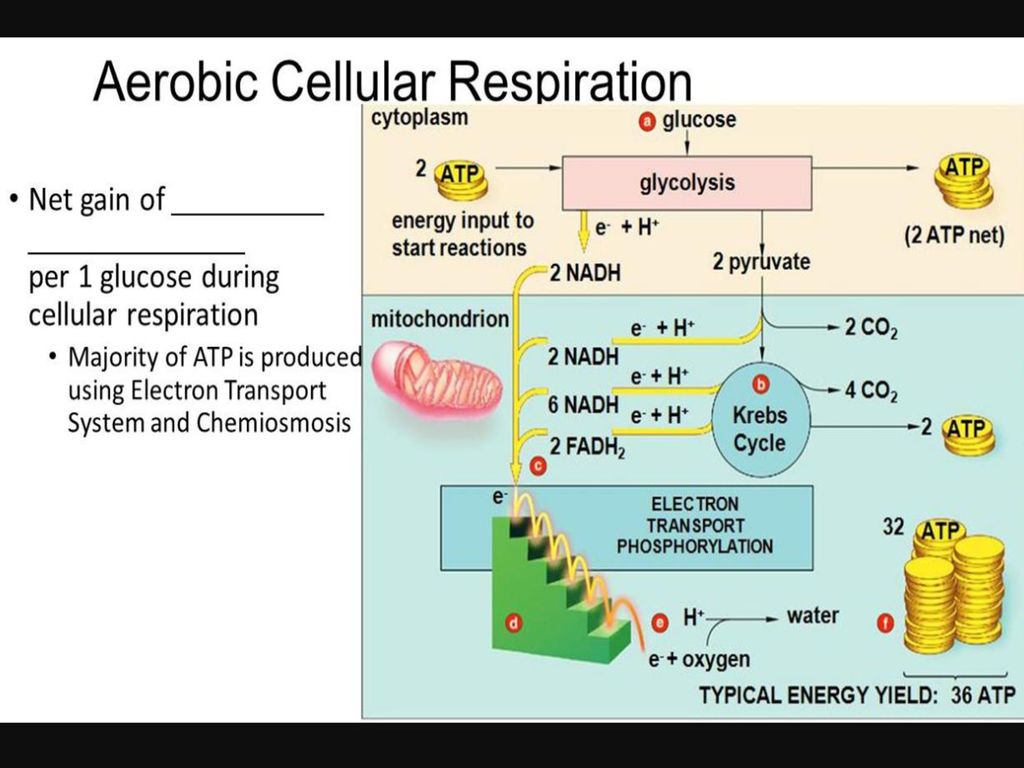
This pathway breaks down 1 glucose molecule and produces 2 pyruvate molecules. The three stages of aerobic cellular respiration are. Cellular Respiration Equation.
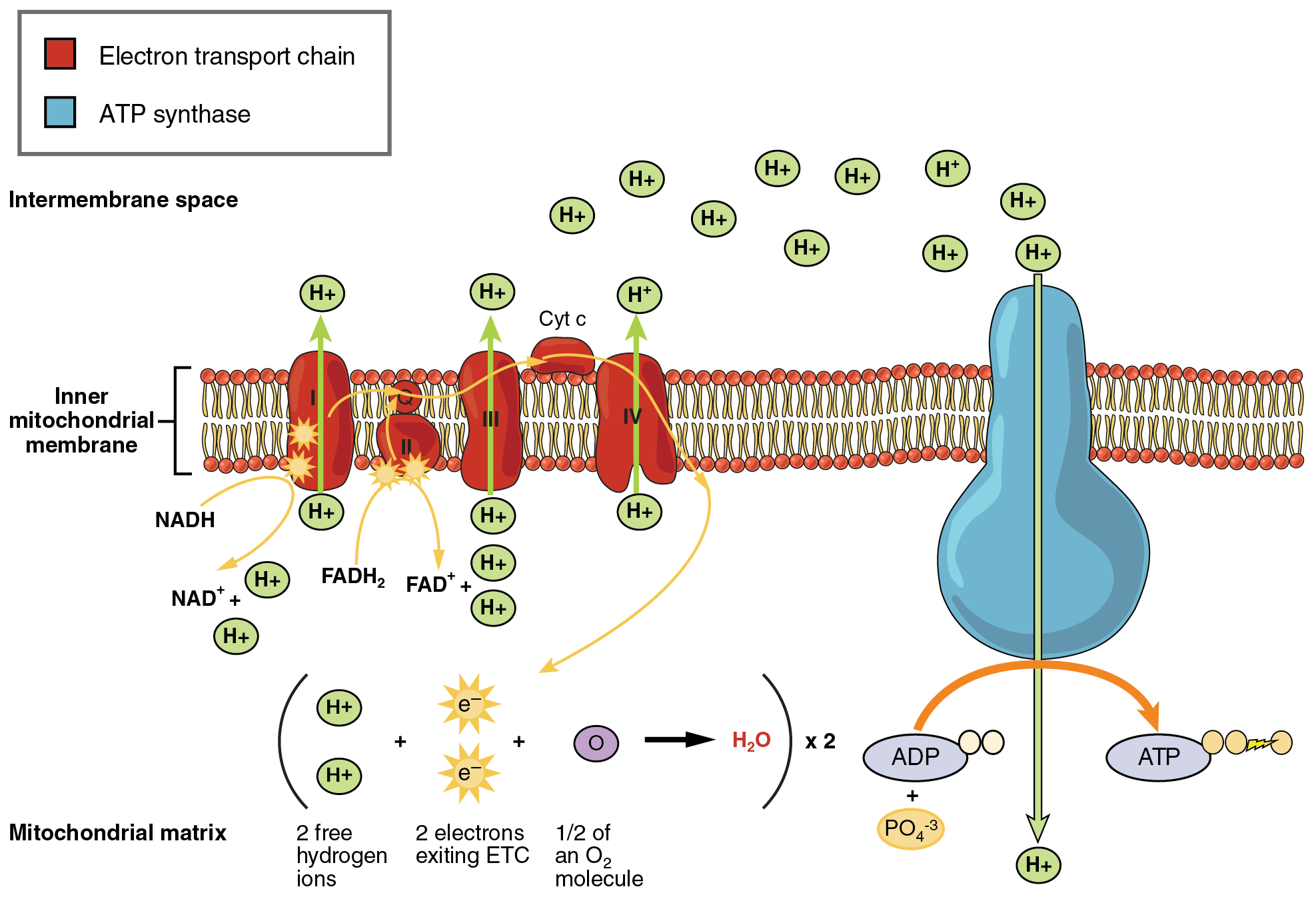
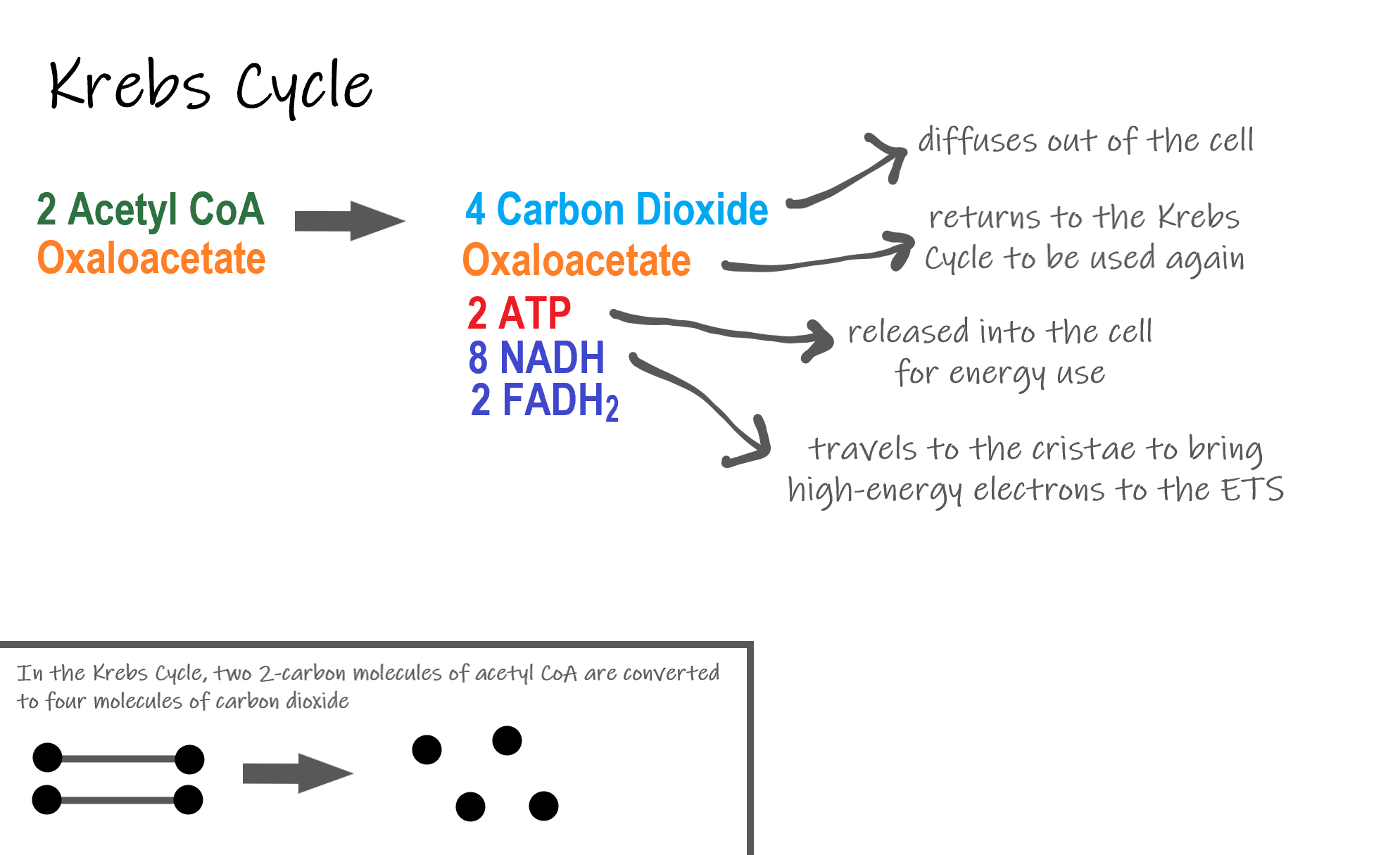
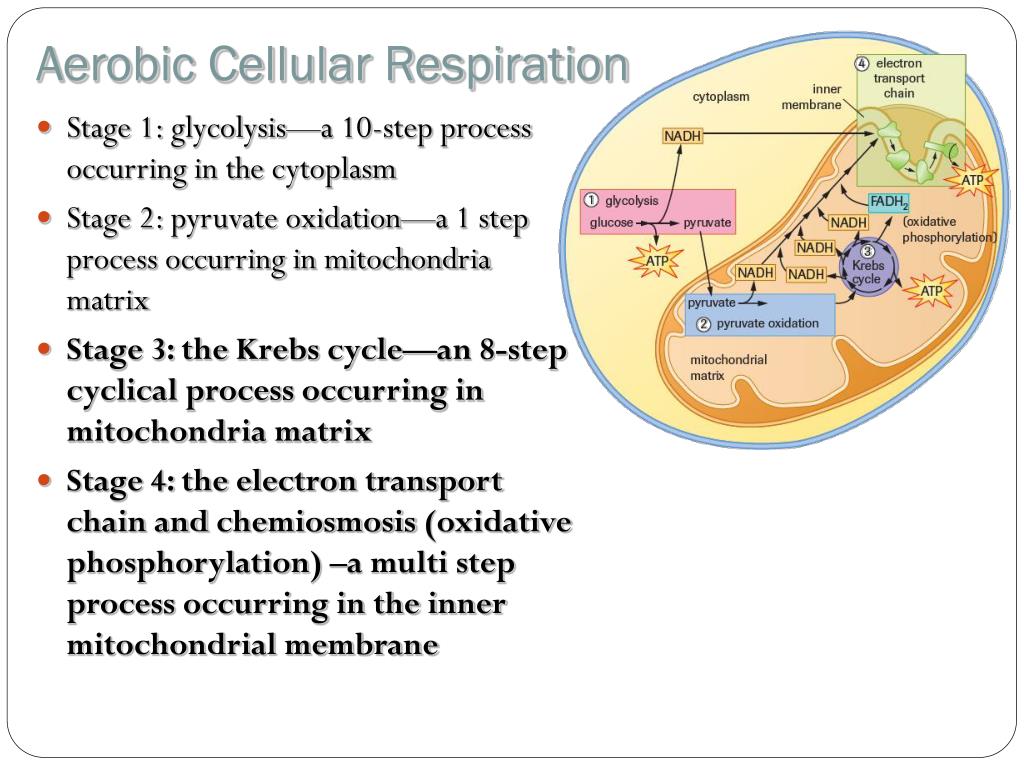
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. The Krebs Cycle which takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. The cellular respiration may be divided into four stages.
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm without oxygen. On the other hand external respiration takes place between the external environment and tissues that are directly involved such as the lungs. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
This type of respiration is common in most of the. This includes the entry of oxygen and the exit of carbon dioxide from the cells. There are three main stages of aerobic respiration glycolysis the Krebs Cycle and the electron transport chain each of which deserves an entire article all to itself but when looking at the overall process of cellular respiration we will only look at these stages at a somewhat basic level leaving out the specific details of every chemical reaction in each stage.
Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cell cytoplasm. The stages in anaerobic respiration are. The other two stages are aerobic processes.









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)
