Food Chain Definition Class 10
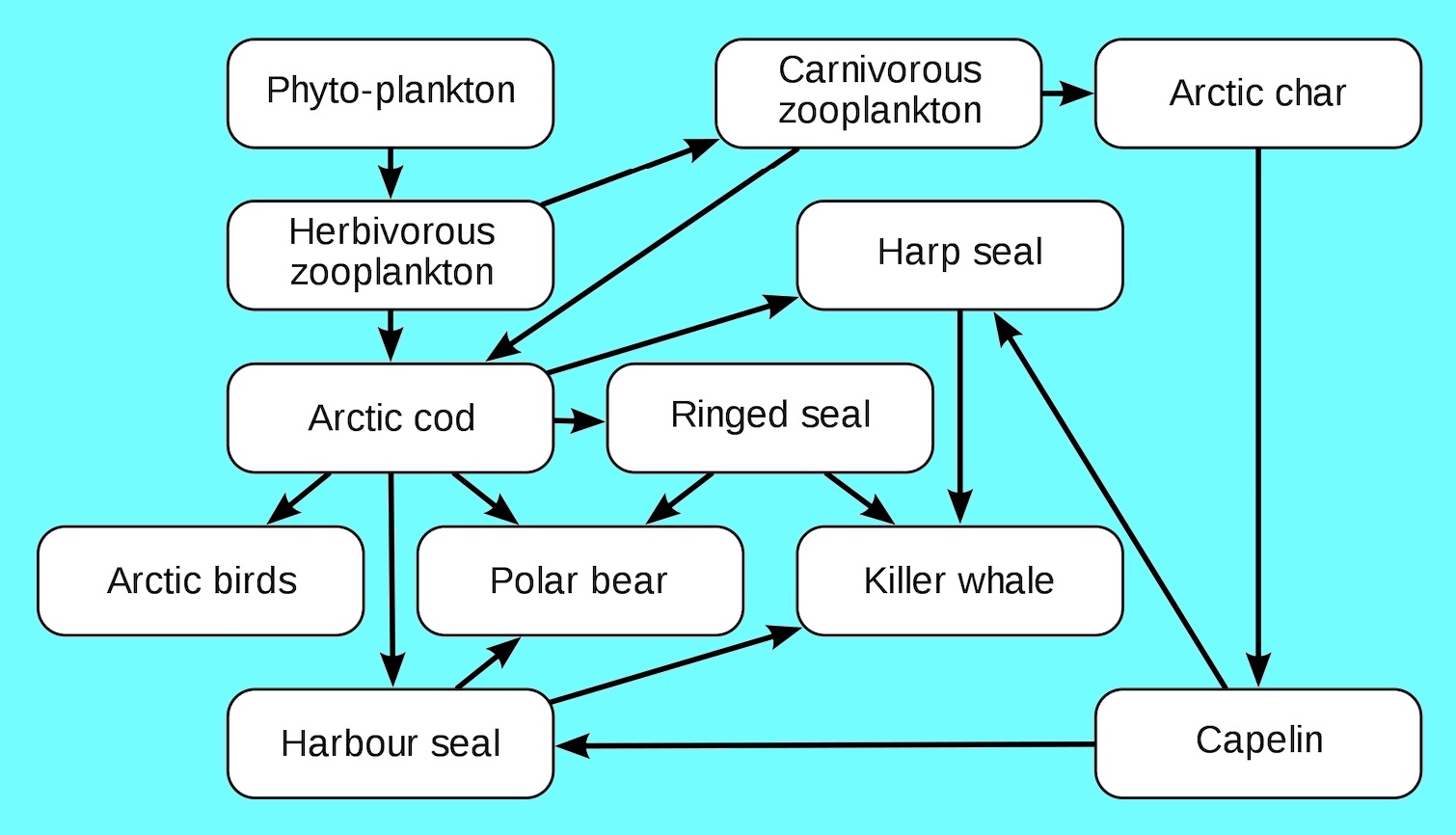
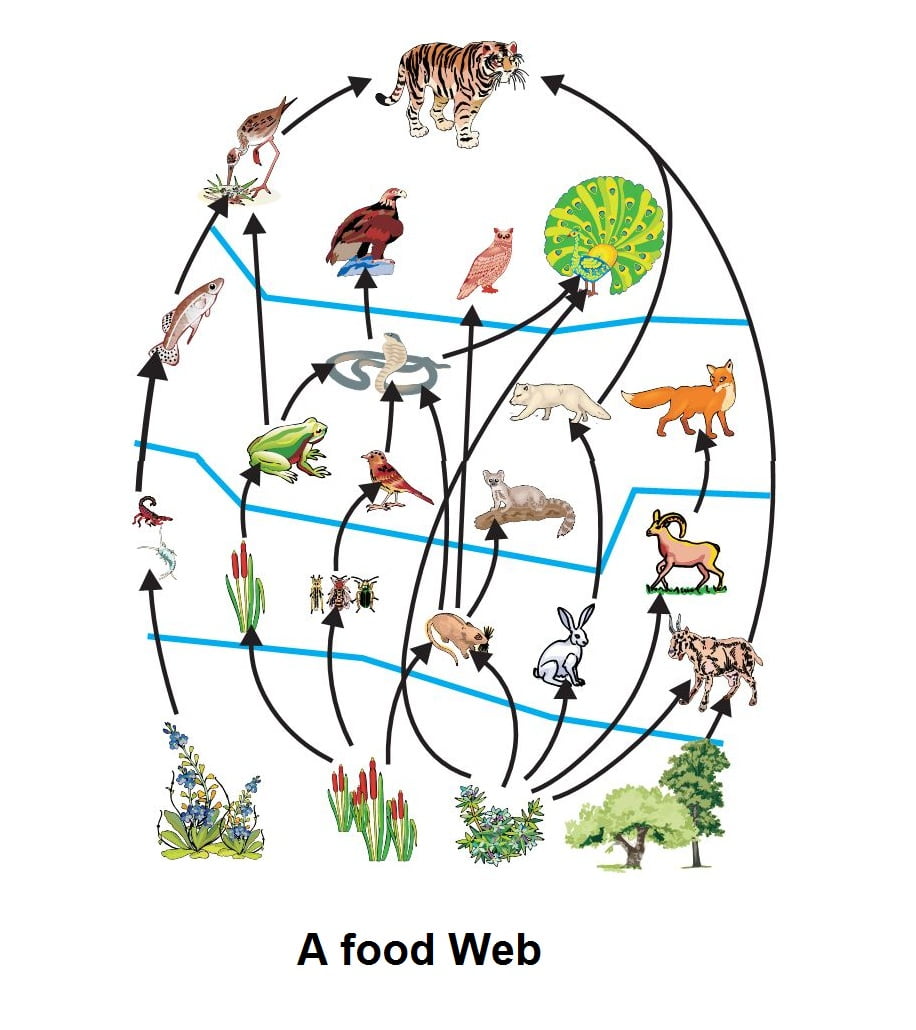
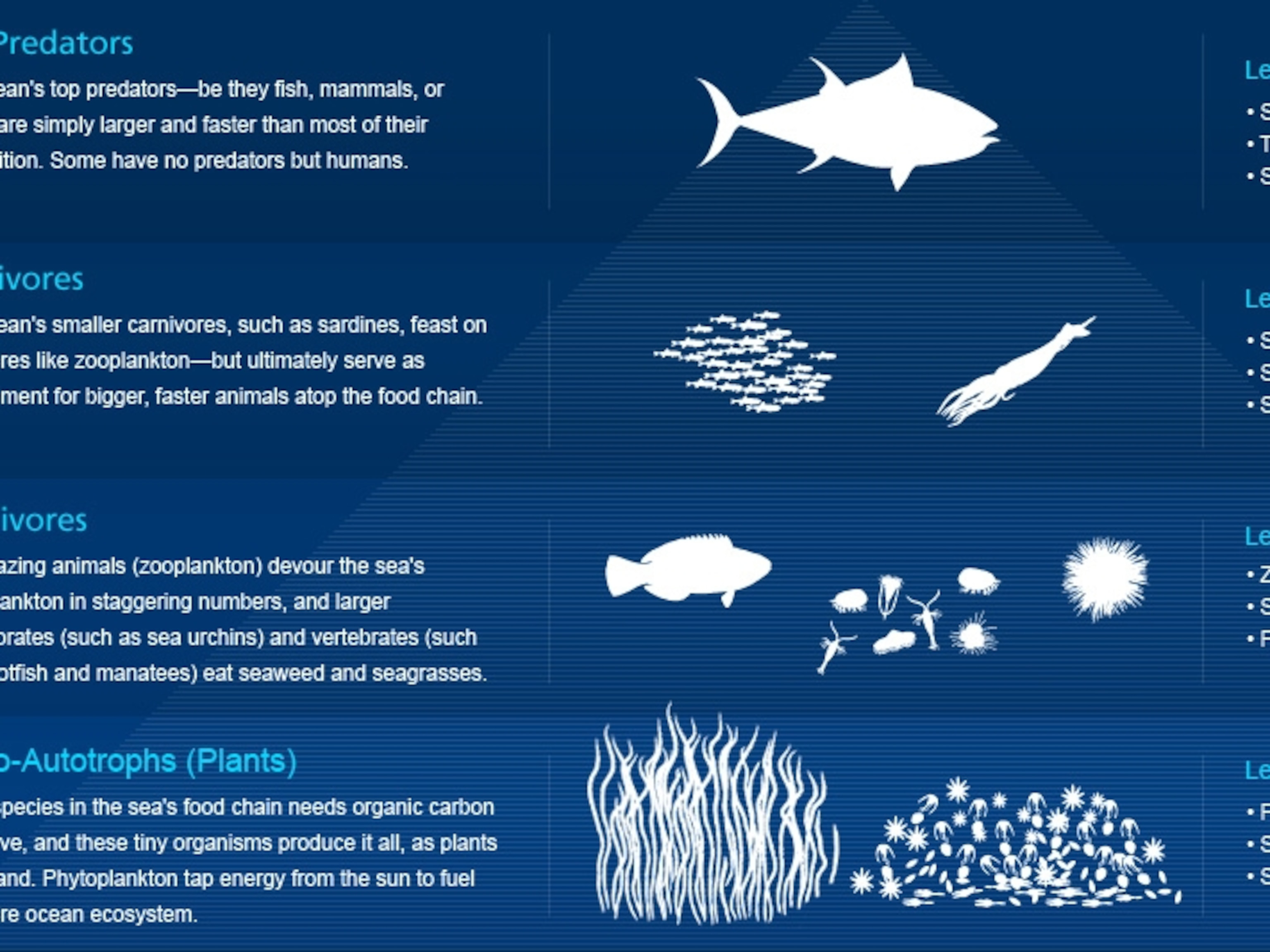
Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant.
Food chain definition class 10. Food chain in ecology the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. A food chain explains which organism eats another organism in the environment. Food Chain Food chain tells us how energy is transferred from one organism to another.
Grazing food chain It starts with autotrophs and goes to consumers. Food webs aid in the understanding of natural selection. In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other.
The chain of organisms which involves transfer of energy from one trophic level to next trophic level is called as food chain. Each step in the food chain is a trophic levelLets took at this food chainSo in this food chainAt the bottom level we have theproducersThey generate food to be eatenExample - PlantsThe organisms that eat the producers are calledPrimary ConsumersThey are Herbivores plant. 2 Energy in the form of food is continuously transferred between different food chains.
Energy is not created or destroyed. Class 10 Biology Our EnvironmentFood chains. Food webs are helpful in explaining how disruptions in populations due to over- hunting poaching global warming and habitat destruction result in food scarcities leading to extinction Trophic level Definition.
Significance of food chain. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. A food chain is always straight and proceeds in a progressive straight line.
In a food chain there is the unidirectional flow of energy from sun to producers and subsequently to series of different types of consumers. A Food chain is basically a linear network of connections in a food web starting from producer organisms or an order of events in an ecosystem where one living organism eats another organism. It is a linear sequence of organisms ie.