Food Chain Definition Ecology

For example grass produces its own food from sunlight.
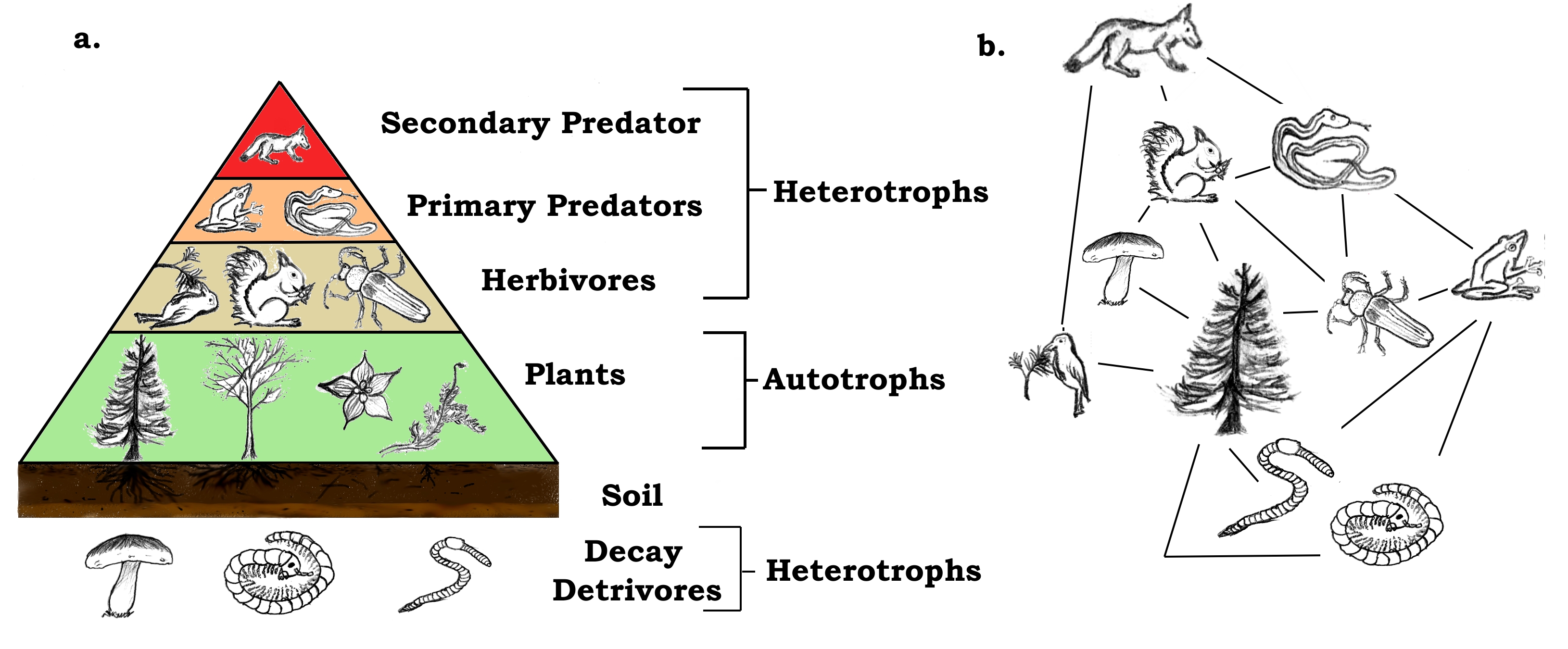
Food chain definition ecology. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaa food chain also shows how the organisms. The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem.
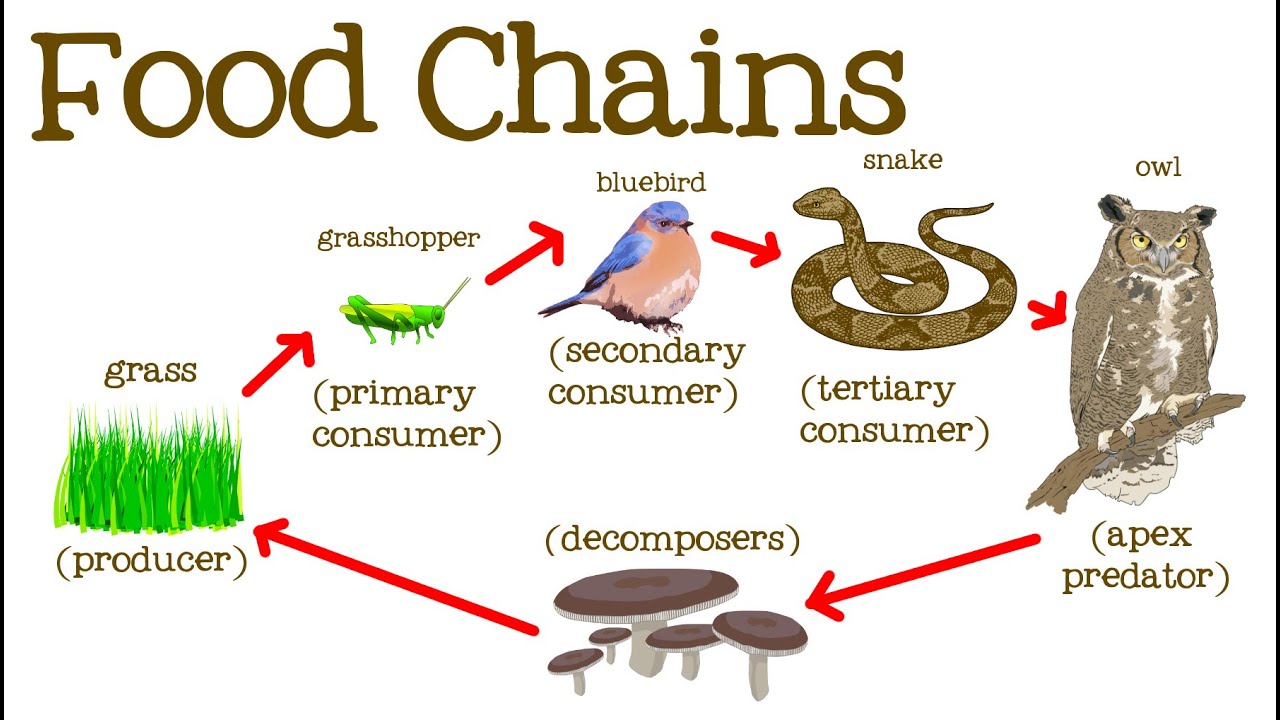
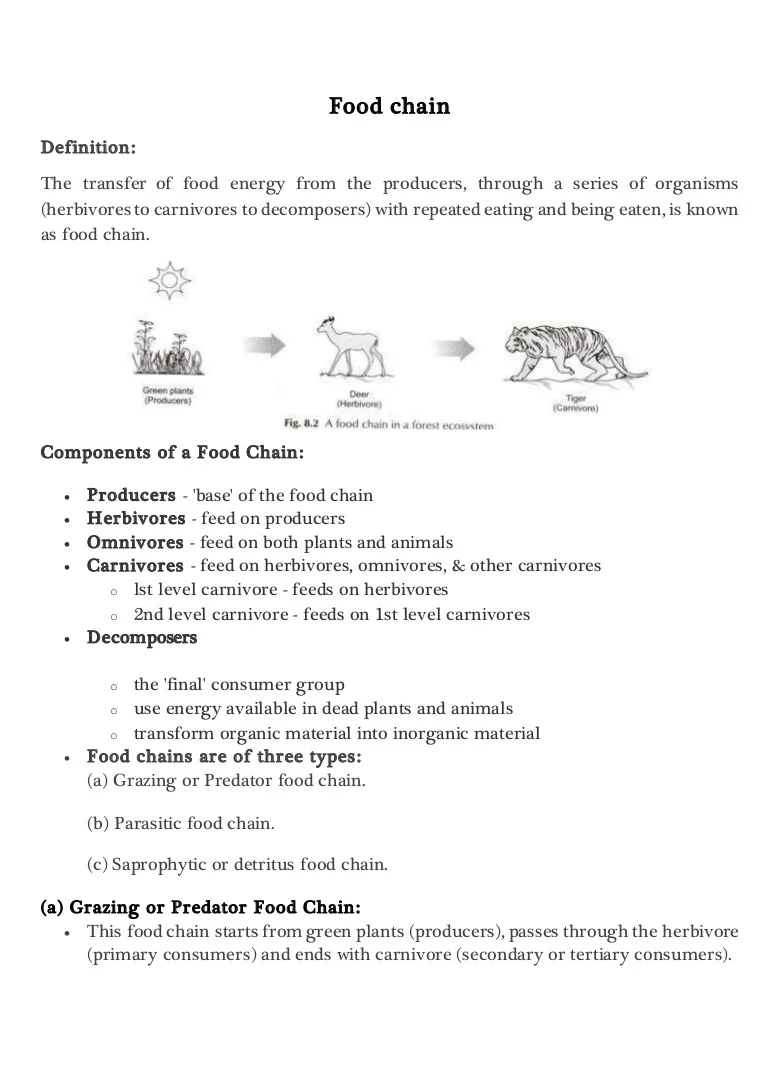
The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83. A food chain shows what eats what in a particular habitat.
The sequence of organism through which the energy flows is known as food chain. Each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrient s can follow through the ecosystem. The pattern of eating and being eaten forms a linear chain called food chain.
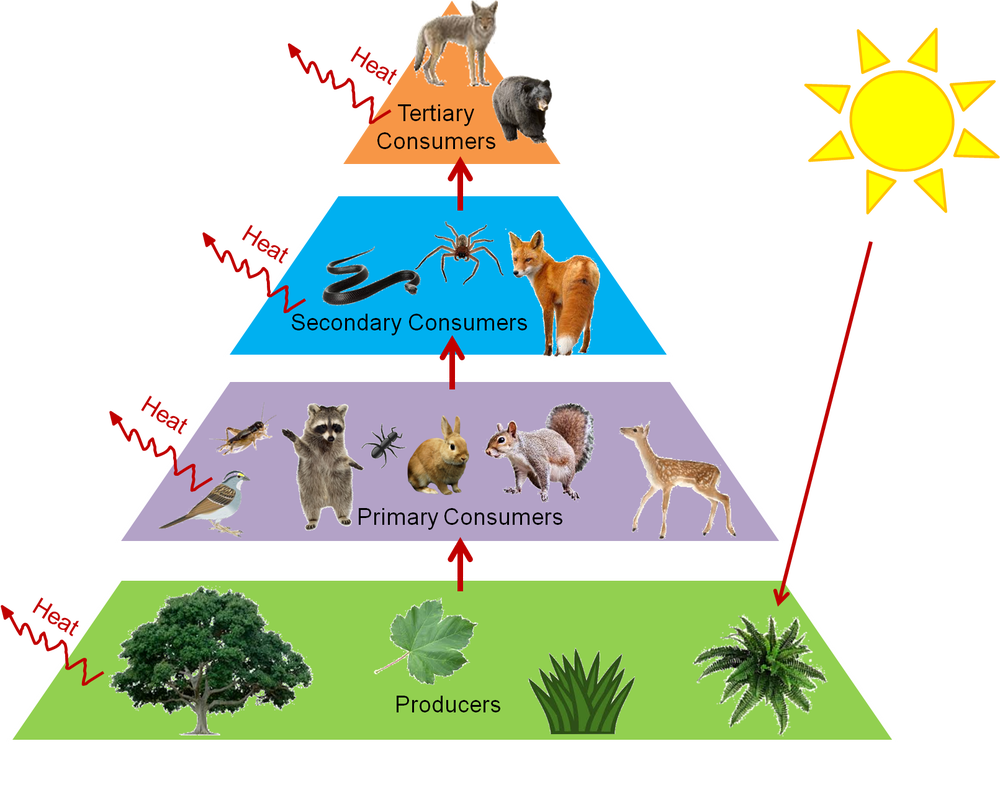
Flow of energy in an ecosystem is one way process. Video about Food Chain Definition Ecology. Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate.
A food chain begins with a producer usually a green plant or alga that creates its own food through photosynthesis. The consumers include all the other types of organisms in the. Forest ecosystem food chain Google Search Forest meaning pronunciation translations and examples.
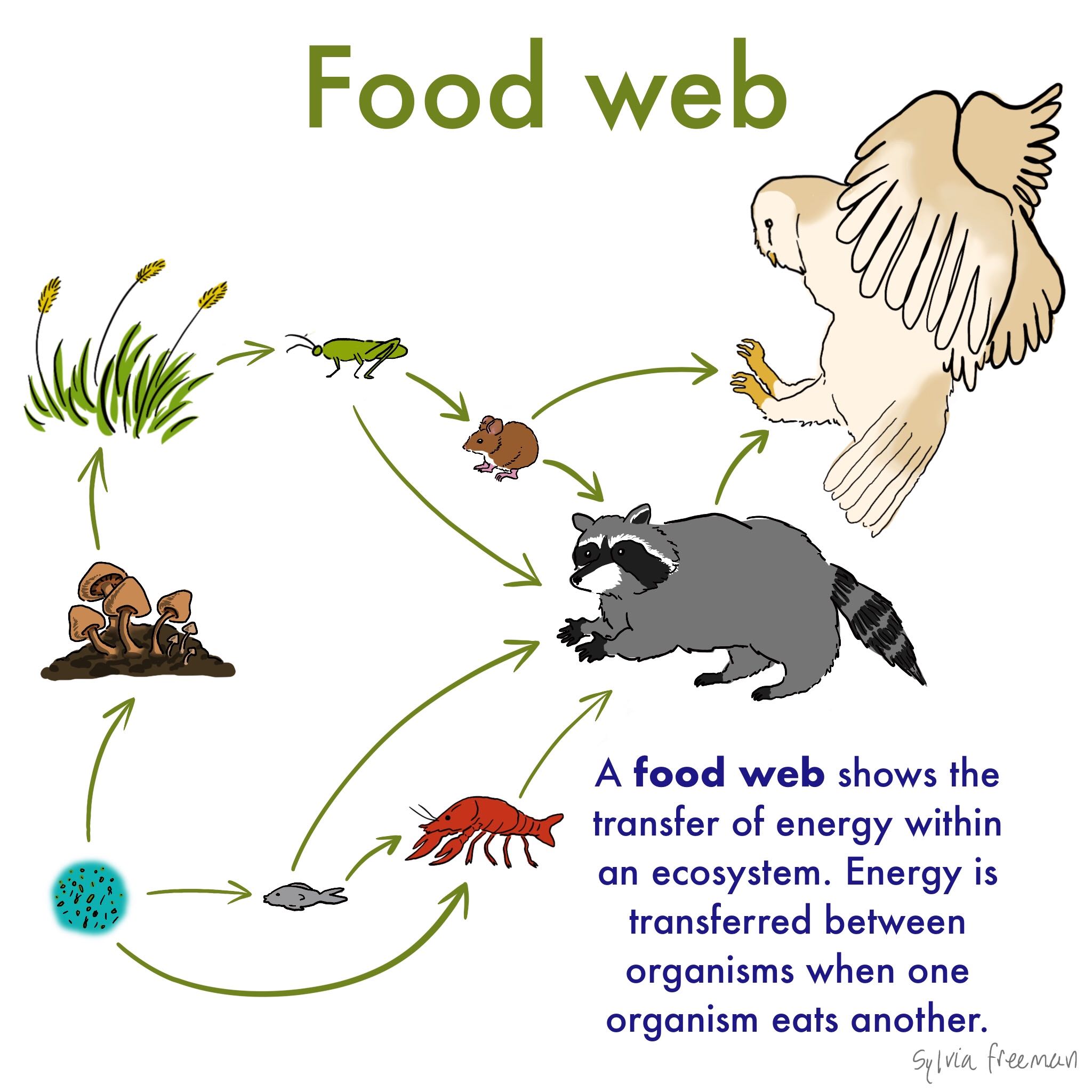
A food web shows multiple food chains multiple relationships and connections. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. Plants are eaten by insects insects are eaten by frogs the frogs are eaten by fish and fishes are eaten by humans.